PlaidCTF 2019 - Horst
13 Apr 2019tldr; Feistel network with constant round key + permutations
Solved with my teammate Tacet.
Description:
They say 3 rounds is provably secure, right?
Task source:
import os
import random
from hashlib import sha1
M = 3
N = 64
n = 2
class Permutation:
def __init__(self, L):
self.n = len(L)
self.L = L
assert all(i in L for i in range(self.n))
def __mul__(self, other):
assert self.n == other.n
return Permutation([other.L[self.L[i]] for i in range(self.n)])
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.L == other.L
def inv(self):
return Permutation([self.L.index(i) for i in range(self.n)])
def cycles(self):
elts = list(range(self.n))
cycles = []
while len(elts) > 0:
cur = []
i = elts[0]
while i not in cur:
cur.append(i)
elts.remove(i)
i = self.L[i]
cycles.append(cur)
return cycles
def __getitem__(self, i):
return self.L[i]
def __str__(self):
return "".join("({})".format(" ".join(str(e) for e in c)) for c in self.cycles())
def __repr__(self):
return "Permutation({})".format(self.L)
def random_permutation(n):
random.seed(os.urandom(100))
L = list(range(n))
for i in range(n-1):
j = random.randint(i, n-1)
L[i], L[j] = L[j], L[i]
return Permutation(L)
for i in range(100):
x = random_permutation(N)
assert x * x.inv() == Permutation(list(range(N)))
def encrypt(m, k):
x, y = m
for i in range(M):
x, y = (y, x * k.inv() * y * k)
return x, y
def decrypt(c, k):
x, y = c
for i in range(M):
x, y = (y * k.inv() * x.inv() * k, x)
return x, y
if __name__ == "__main__":
k = random_permutation(N)
print "The flag is: PCTF{%s}" % sha1(str(k)).hexdigest()
pairs = []
for i in range(n):
pt = random_permutation(N), random_permutation(N)
ct = encrypt(pt, k)
assert pt == decrypt(ct, k)
pairs.append((pt,ct))
with open("data.txt", "w") as f:
f.write(str(pairs))
And data.txt:
[((Permutation([48, 27, 39, 5, 49, 32, 26, 23, 19, 22, 28, 63, 60, 18, 35, 59, 15, 52, 11, 0, 12, 50, 46, 13, 25, 47, 14, 54, 42, 16, 29, 37, 31, 4, 21, 61, 40, 6, 30, 62, 2, 10, 45, 56, 3, 36, 17, 8, 55, 20, 7, 43, 9, 51, 53, 58, 44, 34, 57, 1, 33, 41, 38, 24]), Permutation([28, 34, 61, 25, 57, 56, 59, 7, 6, 27, 62, 0, 54, 10, 36, 23, 21, 38, 35, 40, 30, 45, 60, 55, 22, 5, 52, 29, 11, 17, 44, 31, 63, 42, 41, 51, 20, 3, 13, 14, 46, 37, 2, 48, 32, 26, 15, 33, 19, 49, 50, 4, 8, 47, 43, 16, 1, 53, 39, 12, 24, 18, 58, 9])), (Permutation([5, 13, 36, 51, 3, 63, 59, 53, 45, 52, 37, 10, 39, 15, 41, 16, 57, 49, 34, 21, 40, 2, 44, 55, 6, 24, 43, 23, 48, 25, 8, 60, 26, 62, 19, 12, 33, 7, 29, 30, 27, 18, 0, 46, 61, 11, 50, 4, 32, 38, 54, 17, 14, 35, 42, 9, 47, 20, 28, 31, 56, 58, 1, 22]), Permutation([25, 45, 37, 52, 27, 26, 9, 55, 40, 15, 59, 30, 3, 13, 62, 8, 17, 53, 47, 56, 6, 20, 11, 0, 24, 21, 39, 33, 19, 32, 41, 44, 43, 5, 18, 60, 58, 12, 23, 42, 46, 22, 36, 16, 28, 63, 38, 10, 49, 4, 14, 1, 34, 57, 7, 54, 48, 29, 2, 31, 35, 61, 51, 50]))), ((Permutation([27, 11, 22, 17, 49, 33, 48, 12, 14, 6, 62, 53, 41, 5, 24, 13, 21, 46, 36, 61, 29, 60, 58, 43, 16, 47, 45, 20, 39, 37, 19, 31, 10, 42, 44, 54, 51, 15, 0, 34, 35, 18, 8, 26, 30, 23, 3, 40, 32, 52, 28, 1, 7, 2, 25, 59, 38, 9, 56, 50, 4, 57, 63, 55]), Permutation([50, 62, 22, 26, 33, 21, 35, 23, 53, 45, 47, 24, 41, 10, 38, 31, 2, 15, 55, 32, 34, 1, 25, 49, 52, 6, 37, 58, 7, 19, 29, 17, 16, 3, 4, 11, 63, 8, 27, 0, 59, 18, 54, 12, 61, 39, 13, 28, 20, 51, 36, 42, 9, 56, 46, 60, 30, 5, 48, 57, 43, 40, 14, 44])), (Permutation([63, 61, 38, 9, 30, 51, 39, 33, 45, 24, 0, 5, 17, 6, 23, 20, 49, 22, 18, 29, 37, 59, 28, 31, 36, 26, 2, 13, 53, 52, 34, 19, 25, 44, 16, 27, 43, 55, 8, 42, 12, 21, 62, 46, 7, 4, 56, 35, 41, 10, 3, 11, 57, 50, 15, 14, 48, 40, 60, 1, 47, 32, 54, 58]), Permutation([44, 31, 39, 23, 24, 26, 32, 57, 35, 55, 17, 3, 42, 7, 33, 14, 30, 47, 21, 56, 50, 62, 58, 11, 60, 36, 37, 63, 20, 2, 15, 25, 5, 34, 0, 22, 28, 45, 40, 38, 46, 41, 9, 59, 1, 8, 27, 49, 52, 4, 6, 16, 10, 48, 43, 29, 12, 13, 54, 51, 18, 19, 53, 61])))]
The script implements random permutations of length N. We can compose (multiply) them, compute inversions and get decomposition to cycles.
In [3]: X, Y = random_permutation(N), random_permutation(N)
In [4]: X
Out[4]: Permutation([18, 4, 7, 12, 10, 19, 39, 22, 20, 28, 34, 5, 41, 2, 24, 37, 29, 6, 57, 58, 25, 44, 11, 48, 23, 1, 45, 46, 47, 30, 42, 50, 49, 33, 9, 62, 38, 56, 36, 21, 17, 0, 3, 60, 53, 27, 32, 40, 51, 61, 16, 14, 55, 63, 13, 35, 15, 8, 54, 59, 52, 31, 43, 26])
In [5]: Y
Out[5]: Permutation([61, 21, 24, 37, 32, 63, 60, 29, 52, 40, 13, 56, 23, 54, 36, 2, 1, 11, 16, 55, 50, 31, 41, 18, 12, 51, 4, 57, 6, 10, 59, 20, 39, 5, 3, 27, 26, 49, 38, 17, 43, 44, 14, 48, 47, 42, 28, 62, 35, 15, 0, 8, 9, 19, 7, 25, 58, 33, 46, 34, 45, 53, 22, 30])
In [6]: str(X)
Out[6]: '(0 18 57 8 20 25 1 4 10 34 9 28 47 40 17 6 39 21 44 53 63 26 45 27 46 32 49 61 31 50 16 29 30 42 3 12 41)(2 7 22 11 5 19 58 54 13)(14 24 23 48 51)(15 37 56)(33)(35 62 43 60 52 55)(36 38)(59)'
In [7]: str(Y)
Out[7]: '(0 61 53 19 55 25 51 8 52 9 40 43 48 35 27 57 33 5 63 30 59 34 3 37 49 15 2 24 12 23 18 16 1 21 31 20 50)(4 32 39 17 11 56 58 46 28 6 60 45 42 14 36 26)(7 29 10 13 54)(22 41 44 47 62)(38)'
In [8]: str(X*Y)
Out[8]: '(0 16 10 3 23 35 22 56 2 29 59 34 40 11 63 4 13 24 18 33 5 55 27 28 62 48 8 50 1 32 15 49 53 30 14 12 44 19 46 39 31)(6 17 60 9)(7 41 61 20 51 36 38 26 42 37 58)(21 47 43 45 57 52 25)(54)'
In [9]: str((X*Y).inv())
Out[9]: '(0 31 39 46 19 44 12 14 30 53 49 15 32 1 50 8 48 62 28 27 55 5 33 18 24 13 4 63 11 40 34 59 29 2 56 22 35 23 3 10 16)(6 9 60 17)(7 58 37 42 26 38 36 51 20 61 41)(21 25 52 57 45 43 47)(54)'
We are given two plaintext-ciphertext pairs and are supposed to find encryption key.
The cipher is a 3-round fesitel network.
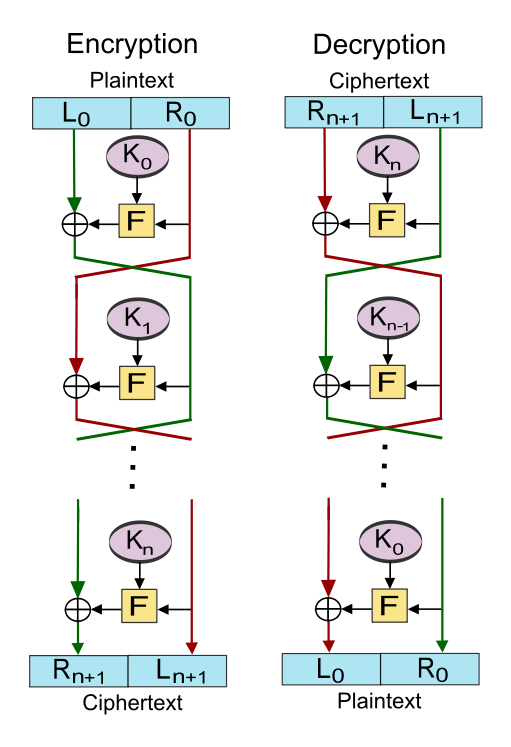 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feistel_cipher
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Feistel_cipher
But instead of plaintext/ciphertext bytes, xor and “normal” round function we have permutations, permutation composition and permutation conjunction.
Given that X, Y are input permutations and K is key permutation, the xor becomes X * K and round function is K.inv() * X * K (where .inv() means inverse, such that X * X.inv() = identity permutation).
The cipher encryption function now looks like this:
X Y
Y X * K.inv() * Y * K
X*K.inv()*Y*K Y * K.inv() * (X*K.inv()*Y*K) * K
Y*K.inv()*(X*K.inv()*Y*K)*K (X*K.inv()*Y*K) * K.inv() * [Y*K.inv()*(X*K.inv()*Y*K)*K] * K
Note about the task description: it is proven that if round function is pseudo-random-function then 3 round feistel cipher using it is pseudo-random-permutation (and 4 round gives us strong PRP). Moreover, ideal block ciphers are equivalent to PRP. Check this for more info.
So how do we break provably secure cipher? By looking what is wrong with it ;) And the bug is that it doesn’t use different round-keys (nor key scheduling).
Now mark X1, Y1 as first plaintext and A1, B1 as first ciphertext (similar notation for the second one).
Compute:
R =
X1.inv() * B1 * B2.inv() * X2 =
X1.inv() * (X1*K.inv()*Y1*K*K.inv()*Y1*K.inv()*X1*K.inv()*Y1*K*K*K) * (X2*K.inv()*Y2*K*K.inv()*Y2*K.inv()*X2*K.inv()*Y2*K*K*K).inv() * X2 =
X1.inv() * (X1*K.inv()*Y1*Y1*K.inv()*X1*K.inv()*Y1*K*K*K) * (X2*K.inv()*Y2*Y2*K.inv()*X2*K.inv()*Y2*K*K*K).inv() * X2 =
X1.inv() * (X1*K.inv()*Y1*Y1*K.inv()*X1*K.inv()*Y1*K*K*K) * (K.inv()*K.inv()*K.inv()*Y2.inv()*K*X2.inv()*K*Y2.inv()*Y2.inv()*K*X2.inv()) * X2 =
(K.inv()*Y1*Y1*K.inv()*X1*K.inv()*Y1) * (Y2.inv()*K*X2.inv()*K*Y2.inv()*Y2.inv()*K)
K.inv() * (Y1*Y1) * (K.inv()*X1*K.inv()*Y1*Y2.inv()*K*X2.inv()*K) * (Y2.inv()*Y2.inv()) * K
And:
Z =
Y1.inv() * A1 * A2.inv() * Y2 =
Y1.inv() * (Y1*K.inv()*X1*K.inv()*Y1*K*K) * (Y2*K.inv()*X2*K.inv()*Y2*K*K).inv() * Y2 =
Y1.inv() * (Y1*K.inv()*(X1*K.inv()*Y1*K)*K) * (K.inv()*K.inv()*Y2.inv()*K*X2.inv()*K*Y2.inv()) * Y2 =
(K.inv()*(X1*K.inv()*Y1) * (Y2.inv()*K*X2.inv()*K)
And:
O = Y1 * Y1 * Z * Y2.inv() * Y2.inv()
Now we have:
R = K.inv() * O * K
So, basically, we reduced the cipher to 1-round network. Now the question is how to find K given R and O?
Turns out that given cycle decomposition of O we have:
O = (a1 a2 af)(b1 b2 bg)...(c1 c2 c3 ch)
K.inv() * O * K = (K(a1) K(a2) K(af))(K(b1) K(b2) K(bg))...(K(c1) K(c2) K(c3) K(ch))
In [6]: O, K = random_permutation(N), random_permutation(N)
In [7]: str(O)
Out[7]: '(48)(0 44 16 52 51 4 13 22 33 1 26 45 18 23 47 41 55 24 50 57 2 21 27 30 14 38 32 40 8 42)(3 35 63 46 12 53 10 20 7 58 49 6)(5 28 15 19 25 61 9 54 17 11 34)(29 56 60 59 36 37 31 43)(39 62)'
In [8]: str(K.inv()*O*K)
Out[8]: '(42)(0 30 52 3 23 5 17 35)(1 20 26 40 2 27 19 37 43 45 44 15 49 25 13 50 29 57 31 34 41 54 59 56 38 24 11 8 62 12)(4 58 7 21 60 51 55 48 47 36 6 33)(9 32 10 53 61 28 46 39 16 22 63)(14 18)'
In [10]: K[48]
Out[10]: 42
In [9]: K[0]
Out[9]: 15
Now the problem is how do we match cycles and elements in the cycles (note that K[0]=15, not 1, because same cycle may have many representations)?
The algorith I used is simple bruteforce:
- decompose O and R into cycles
- for every matching cycles (cycles of the same length) try every possible element as the first in the cycle
- reconstruct whole key
- check if it correctly decrypts given ciphertexts
Solution:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
~Gros
'''
from horst import *
def match_one_cycle(c_cycles, y_cycle):
for c_cycle in c_cycles:
if len(c_cycle) == len(y_cycle):
for start_pos in range(0, len(c_cycle)):
yield (c_cycle, c_cycle[start_pos:] + c_cycle[:start_pos])
def test_k(k, pairs):
for pair in pairs:
pt,ct = pair
if pt != decrypt(ct,k):
return False
return True
def sr(n, c, y, c_cycles, y_cycles, k, pairs):
if len(c_cycles) == 0:
k = Permutation(k)
if test_k(k, pairs):
print('found!')
yield k
else:
yield False
return
for c_cycle, c_cycle_match in match_one_cycle(c_cycles, y_cycles[0]):
k2 = k[:]
for j in range(len(y_cycles[0])):
k2[y_cycles[0][j]] = c_cycle_match[j]
y_cycles_smaller = y_cycles[1:]
c_cycles_smaller = c_cycles[:]
c_cycles_smaller.remove(c_cycle)
for job_done in sr(n, c, y, c_cycles_smaller, y_cycles_smaller, k2, pairs):
if job_done:
yield job_done
def solve_conjugacy(c, y, pairs):
"""
c = k.inv()*y*k
find: k
"""
k = [i for i in range(c.n)]
c_cycles = c.cycles()
y_cycles = y.cycles()
for k2 in sr(c.n, c, y, c_cycles, y_cycles, k, pairs):
assert (k2.inv() * y * k2) == c
yield k2
def test_solve_conjugacy():
k = random_permutation(30)
y = random_permutation(30)
c = k.inv() * y * k
k2 = solve_conjugacy(c, y, pairs)
print(k, k2)
assert k == k2
def test():
N = 30
k = random_permutation(N)
pairs = []
for i in range(n):
pt = random_permutation(N), random_permutation(N)
ct = encrypt(pt, k)
assert pt == decrypt(ct, k)
pairs.append((pt,ct))
p1, p2 = pairs
print('encrypted')
pt1, ct1 = p1
x1, y1 = pt1
a1, b1 = ct1
pt2, ct2 = p2
x2, y2 = pt2
a2, b2 = ct2
r = x1.inv() * b1 * b2.inv() * x2
o = y1.inv() * a1 * a2.inv() * y2
o = y1 * y1 * o * y2.inv() * y2.inv()
assert k.inv() * o * k == r
print('solving conjugacy')
for k2 in solve_conjugacy(r, o, pairs):
assert str(k) == str(k2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# test()
with open('data.txt', 'rb') as f:
p1, p2 = eval(f.read())
pt1, ct1 = p1
x1, y1 = pt1
a1, b1 = ct1
pt2, ct2 = p2
x2, y2 = pt2
a2, b2 = ct2
r = x1.inv() * b1 * b2.inv() * x2
o = y1.inv() * a1 * a2.inv() * y2
o = y1 * y1 * o * y2.inv() * y2.inv()
for k in solve_conjugacy(r, o, [p1,p2]):
print('key', k)
assert pt1 == decrypt(ct1, k)
assert pt2 == decrypt(ct2, k)
print "The flag is: PCTF{%s}" % sha1(str(k)).hexdigest()
# PCTF{69f4153d282560cdaab05e14c9f1b7e0a5cc74d1}
